The GNU Project Debugger (GDB): Short Tutorial with Examples

GDB, also called The GNU Project Debugger, identifies problems like segmentation faults in a code. It helps you to determine where the problem lies and what the program is doing at a particular instance. It can be run on the native machine, remote machine, or on any simulator.
Official website: https://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/
Download Link: https://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/download/
Installation (Linux)
$sudo apt-get install gdb

As it is already installed, it gives the above message.
Languages supported by GDB.
Ada, Assembly, C, C++, D, Fortran, Go, Objective-C, OpenCL, Modula-2, Pascal, and Rust.
Help in GDB
$gdb -h



Examples using gdb for debugging
Example 1
Step 1: Create C (hello.c) Hello World program by typing below command
$gedit hello.c
On the opening of gedit screen, type a simple program of hello world and save it.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Hello World\n");
}

Step 2: Compile the program
$gcc -g hello.c -o hello
Step 3: Execute the program
$./hello

Step 4: Start debugging by writing the below command
$gdb hello

To run a program:
(gdb)run

As the program is clean (no segmentation error like an issue) and no error, it should give output; otherwise, give some information related to the issue where the program lies.
Example 2
Step 1: Create C (testgdb.c) program by typing below command
$gedit testgdb.c
On the opening of gedit screen, type a simple program of the division of two numbers (x = 10, y = 0) and save it.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x = 10, y = 0;
int z;
z = x/y;
printf("z =", z);
}
Step 2: Compile the program. As we are dividing 10 by 0, it gives a compilation error.
$gcc -g testgdb.c -o testgdb

Step 3: Start debugging by writing the below command
$gdb testgdb
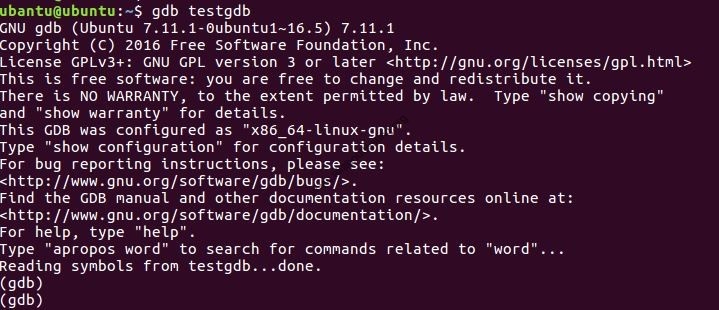
Step 4: To run a program.

Basically, we don't need gdb if the program is running without any issue. As this program has a problem, we will resolve an issue with the help of gdb.

Breakpoints used to stop the program in the middle, and in the below snapshot used, "break 7" has a problem. The run "r" command is used to run the program again, generating an error. Print x and y value by using "print x" and "print y."

"next" or "n" is used for next line execution of the current stack frame. In simple terms, this command is used to execute the next line of code during runtime.
(gdb)next
Now we can use the below commands to assign different values while executing of code.
(gdb)set variable y = 2 #assigning value during execution
The below command is used to produce the disassembly output of the function.
(gdb)disassemble main

Exit from GDB:
Following command is used to "quit" or "q" the gdb
(gdb)quit
Subscribe us to receive more such articles updates in your email.
If you have any questions, feel free to ask in the comments section below. Nothing gives me greater joy than helping my readers!
Disclaimer: This tutorial is for educational purpose only. Individual is solely responsible for any illegal act.