Top 20 Windows PowerShell Commands for Administrators

Windows PowerShell is a command-line shell of a Windows system. It helps in the automation of tasks and processes of the different operating systems such as Linux, Windows, and macOS.
To open a PowerShell, just search PowerShell on Windows, right-click, and click on the run as administrator. Here, we will list out the top 20 PowerShell commands that help you understand and use commands more.
Top 20 Windows PowerShell Commands for Administrators
(1) Get-Help command helps the user identify the usage of cmdlets, functions, scripts, and modules. In simple terms, you can extract all information and usage of commands by using this cmdlet
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Get-Help

Usage Examples:
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Get-Help <command> PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Get-Help <command> -Example PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Get-Help <command> -Full PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Get-Help *
(2) To update the help content of PowerShell
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Update-Help


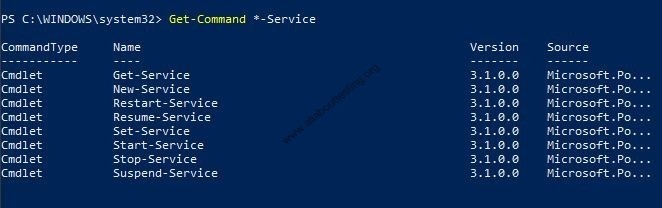
(3) Get-Command displays all commands available in PowerShell. In the below example, the command used with wildcard * to display commands with the suffix Service
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Get-Command *-Service
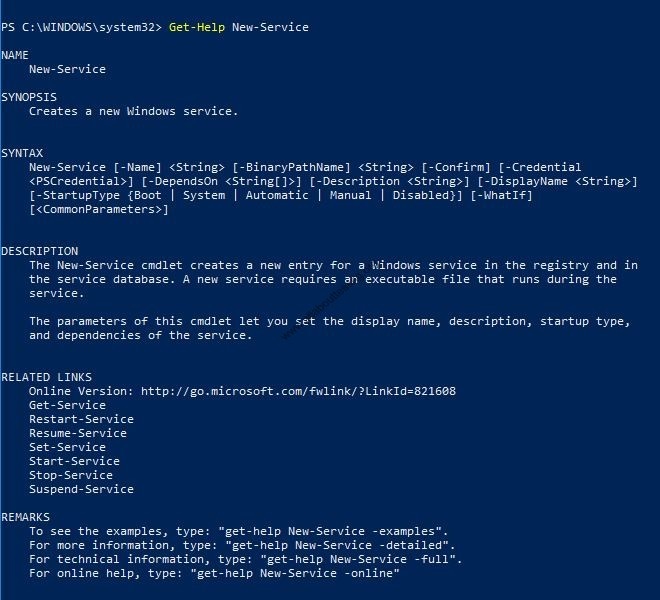
(4) Get-Help command used to understand the usage of commands
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Get-Help New-Service
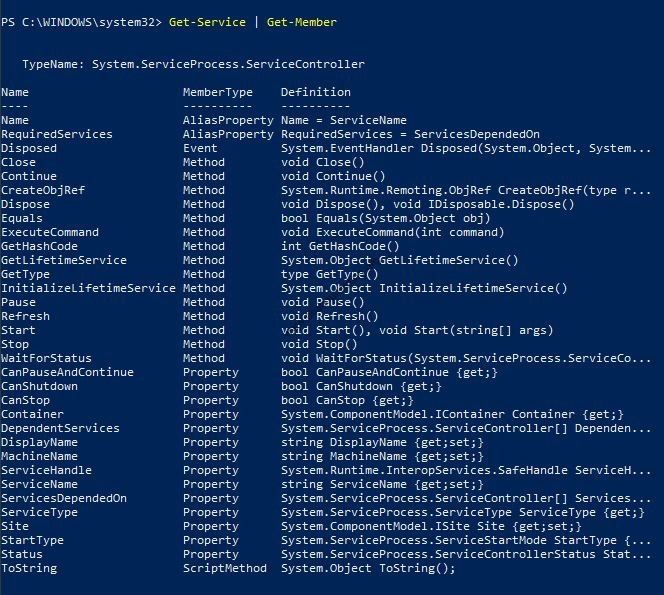
(5) Get-Service command used to display the running and stopped services of the computer. It may be used with wildcards to filter content specific to the search element
In addition, the Get-Member command displays the members, properties, and methods, of objects.
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Get-Service | Get-Member
(6) To clear the screen or window of PowerShell. You may alternately use alias cls or clear
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Clear-Host
(7) Get-Alias command helps to find the exact name of the PowerShell command
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Get-Alias history

Some commands of cmd and Linux may use in PowerShell also.
1) cat 2) dir 3) mount 4) rm 5) cd 6) echo 7) move 8) rmdir
9) chdir 10) erase 11) popd 12) sleep 13) clear 14) h 15) ps
16) sort 17) cls 18) history 19) copy 20) kill 21) pwd 22) type
23) del 24) lp 25) r 26) write 27) diff 28) ls
(8) To create a user given an alias to a specific command
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Set-Alias -Name hj -Value Get-Location

(9) Create a variable to access the commands
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> $loc = Get-Location PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> $loc

(10) Comparison operators ( eq (equals), ne (not equals), gt (greater than), ge (greater than or equals to), lt (less than), le (less than or equals to))
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> $A = 1 PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> $B = 8 PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> $A -eq $B

PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> $A -ne $B PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> $A -gt $B PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> $A -ge $B PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> $A -lt $B PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> $A -le $B

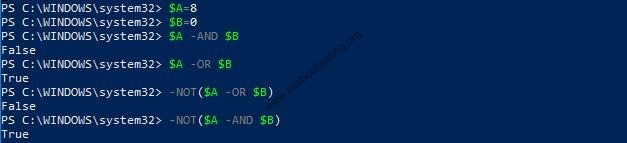
(13) Logical operators (-AND (logical and), -OR (logical or), -NOT (logical not)) used to perform boolean expression
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> $A -AND $B PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> $A -OR $B PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> -NOT($A -AND $B) PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> -NOT($A -OR $B)
(14) Arithmetic operators ( + (addition), - (subtraction), * (multiplication), / (division), % (modulus)) to perform mathematical operations

(15) To store results in a text file by using > operator
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> dir > test.log
(16) Get-ChildItem command displays all directories and sub-directories
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Get-ChildItem
Below command lists out directories up to depth 2
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Windows -Depth 2
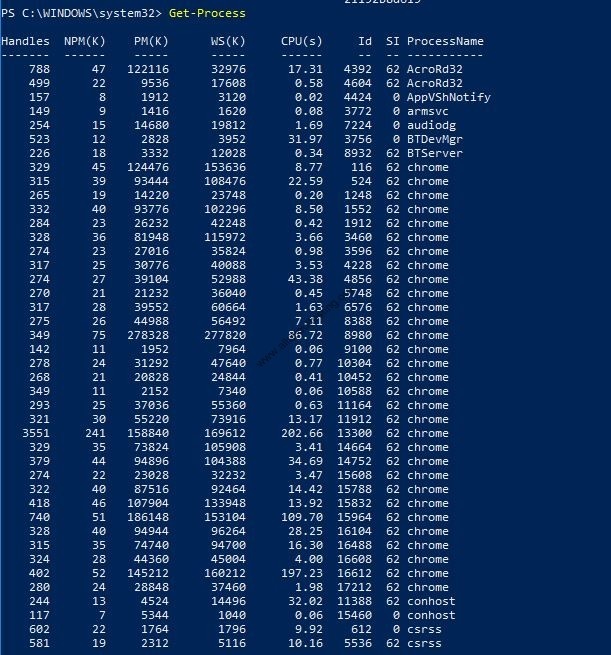
(17) Get-Process command is used to list out processes on a local computer
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Get-Process
(18) Restart-Service command is used to stop and again start the service on a computer
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Restart-Service -Name Themes
(19) The Remove-Item command is used to delete all files within a directory without being prompted for each deletion
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Remove-Item C:\test –Recurse
(20) To display the top 20 updated processes list sorted by CPU by using while loop functionality
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> while (1) { ps | sort -desc cpu | select -first 20; sleep -seconds 10; cls }

Subscribe us to receive more such articles updates in your email.
If you have any questions, feel free to ask in the comments section below. Nothing gives me greater joy than helping my readers!
Disclaimer: This tutorial is for educational purpose only. Individual is solely responsible for any illegal act.








